-
UK needs £102bn boost to NHS and social care, says major report

Funding from higher taxes would cut avoidable deaths and improve equality after the Covid pandemic
Spending on the NHS, social care and public health needs to rise by £102bn over the next decade, funded by big tax rises, to improve Britain’s health in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, an inquiry has said.
The massive funding boost would cut avoidable deaths from cancer and heart disease, tackle glaring health inequalities and rebuild the NHS after Covid exposed weaknesses such as a lack of beds and staff, a team of experts urged ministers on Friday.
The money would come largely from increases in income tax, national insurance and VAT, which evidence suggests the public is willing to pay, according to a four-year commission of inquiry by the London School of Economics and the Lancet medical journal.
“Without concerted action and increased funding we risk the UK falling further behind other high-income countries in health outcomes and life expectancy, continued deterioration in service provision and worsening inequalities, increased reliance on private funding and an NHS that is poorly equipped to respond to future major threats to health,” said Dr Michael Anderson of the LSE, the commission’s joint research lead.
The government must seize on the pandemic as an opportunity to transform the NHS, social care and public health so that they can drive much-needed improvements to the nation’s health, which still lags behind that in many other high-income countries in key respects, the 33 health experts involved said in a 123-page report that also assesses the health service’s response to Covid.
In the report, which they describe as “a call to action”, they called for UK spending in those three areas combined to increase dramatically from £185bn today to £288bn by 2030/31, with every sector getting a 4% budget uplift for each of the next 10 years. Under their plans, the NHS budget across the four home nations would soar from £162bn to £239bn.
Their blueprint envisages the extra money coming in two major phased rounds of tax rises: 1p on income tax, national insurance and VAT by 2025-26 and then a further 2p increase in both income tax and NICs, plus another 1p on VAT, by 2030-31. That would mean someone on £25,000 a year paying an extra £6 a week, and someone on £50,000 an additional £15 a week, by 2025/26.
The plan has been drawn up by two highly rated economists: Paul Johnson, director of the Institute for Fiscal Studies, and Prof Anita Charlesworth, director of research and economics at the Health Foundation.
Such unprecedented budget increases across the three sectors are needed “to ensure that the health and care system can meet demand, rebuild after the pandemic and develop resilience against further acute shocks and major threats to health”, the commissioners said. But they recognise that persuading ministers to approve such hefty rises will be “challenging in economically and geopolitically uncertain times”.
“For the NHS to be truly the envy of the world again politicians will need to be honest with the public that this will require increased taxation to meet funding levels of other comparable high-income countries,” said Prof Elias Mossialos of the LSE, the commission’s co-chair.
The report highlighted how, despite being the world’s fifth largest economy, Britain comes only ninth in an international league table of health spending as judged by the proportion of GDP invested, its 10.35% coming behind Germany (11.7%), France (11.2%) and Japan (11.1%). Judged by health spending per head, the UK comes 13th, based on allocating £3,620 per person.
The report also:
Warns Boris Johnson to drop his planned reorganisation of the NHS in England, which will feature in next week’s Queen’s speech, which it said will be disruptive and bring no benefits.
Urges ministers and the NHS to ramp up efforts to stop people succumbing to preventable illnesses in the first place by cracking down on smoking, drinking and poor diet.
Proposes an end to the serious staff shortages affecting most parts of the NHS, especially in England, through the creation of a sustainable supply of healthcare workers.
Social care should be reformed to make it easier for Britain’s ageing population to access by increasing the level of savings someone can have before they are charged from £23,250 to £100,000, and by capping lifetime care costs at £75,000. Johnson has reportedly dropped plans to overhaul social care from the Queen’s speech, despite his pledge when he entered No 10 in 2019 to “fix” it with a plan which was ready to be implemented. Downing Street insists the plans are due to be announced this year.
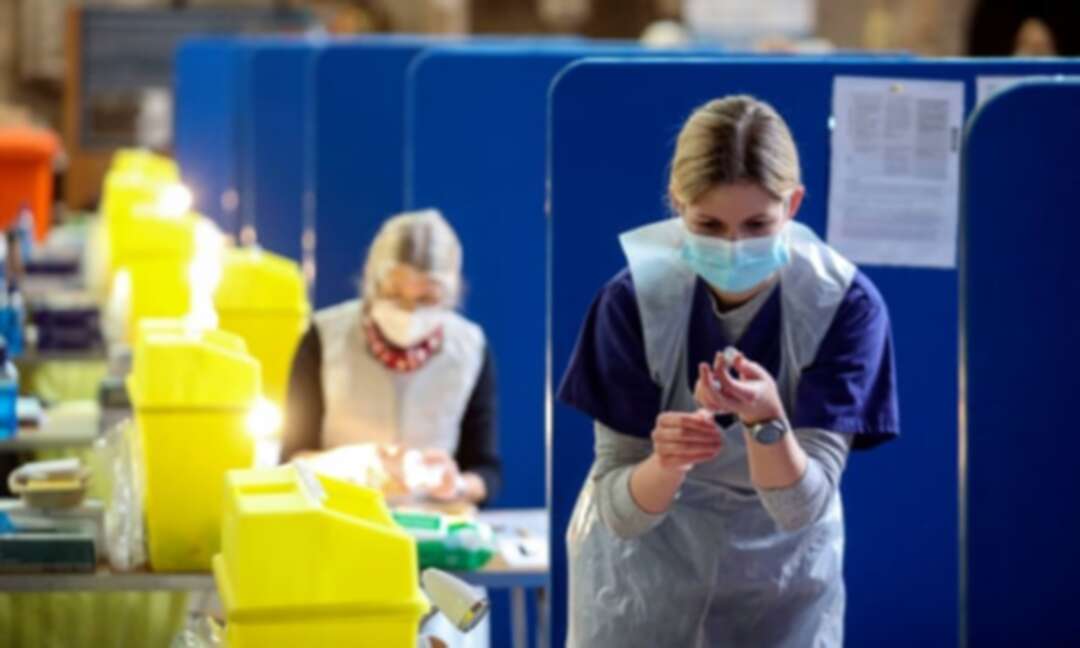
In the first comprehensive assessment of how the NHS responded to Covid, the LSE/Lancet report praises its rapid expansion of intensive care capacity, redeployment of staff to look after patients fighting for their lives, innovations in treatment and the delivery of the Covid vaccination programme.
But Dr Emma Pitchforth, the joint research lead, said that “during the pandemic the NHS has struggled in the face of poor decision-making by government, including delayed implementation of social distancing measures, poor coordination with local authorities and public health teams
Covid also exposed “chronic weaknesses” in the NHS, including low numbers – by international standards – of doctors, nurses, hospital beds and scanners used to diagnose diseases like cancer, the report said.
But Sally Warren, director of policy at the influential King’s Fund thinktank, said tax rises were highly unlikely under Boris Johnson.
“This government has manifesto commitments to not increase income tax, national insurance or VAT. Public polling has often shown that people support increases in taxation to support the NHS, but it is less clear if that extends to related services such as social care and public health.
“If not, there is a risk of repeating the mistakes of the last decade, which saw NHS funding prioritised but spending on other services that promote health and wellbeing neglected. This meant that improvements in life expectancy stalled, inequalities widened and demand for NHS services soared.”
A Department of Health and Social Care spokesperson said: “Our NHS has faced huge challenges over the past year due to Covid-19 and we continue to support our incredible health and care staff who have kept services open for thousands of patients.
“We have made £63bn available for health services over the last year and an additional £29bn next year, including new investment to address backlogs and tackle long waiting lists which have built up because of the pandemic.
“Improving adult social care remains a priority for this government and we will bring forward proposals later this year,” the spokesperson added.
source: Denis Campbell
Levant
You May Also Like
Popular Posts
Caricature
BENEFIT Sponsors BuildHer...
- April 23, 2025
BENEFIT, the Kingdom’s innovator and leading company in Fintech and electronic financial transactions service, has sponsored the BuildHer CityHack 2025 Hackathon, a two-day event spearheaded by the College of Engineering and Technology at the Royal University for Women (RUW).
Aimed at secondary school students, the event brought together a distinguished group of academic professionals and technology experts to mentor and inspire young participants.
More than 100 high school students from across the Kingdom of Bahrain took part in the hackathon, which featured an intensive programme of training workshops and hands-on sessions. These activities were tailored to enhance participants’ critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving, and team-building capabilities, while also encouraging the development of practical and sustainable solutions to contemporary challenges using modern technological tools.
BENEFIT’s Chief Executive Mr. Abdulwahed AlJanahi, commented: “Our support for this educational hackathon reflects our long-term strategic vision to nurture the talents of emerging national youth and empower the next generation of accomplished female leaders in technology. By fostering creativity and innovation, we aim to contribute meaningfully to Bahrain’s comprehensive development goals and align with the aspirations outlined in the Kingdom’s Vision 2030—an ambition in which BENEFIT plays a central role.”
Professor Riyadh Yousif Hamzah, President of the Royal University for Women, commented: “This initiative reflects our commitment to advancing women in STEM fields. We're cultivating a generation of creative, solution-driven female leaders who will drive national development. Our partnership with BENEFIT exemplifies the powerful synergy between academia and private sector in supporting educational innovation.”
Hanan Abdulla Hasan, Senior Manager, PR & Communication at BENEFIT, said: “We are honoured to collaborate with RUW in supporting this remarkable technology-focused event. It highlights our commitment to social responsibility, and our ongoing efforts to enhance the digital and innovation capabilities of young Bahraini women and foster their ability to harness technological tools in the service of a smarter, more sustainable future.”
For his part, Dr. Humam ElAgha, Acting Dean of the College of Engineering and Technology at the University, said: “BuildHer CityHack 2025 embodies our hands-on approach to education. By tackling real-world problems through creative thinking and sustainable solutions, we're preparing women to thrive in the knowledge economy – a cornerstone of the University's vision.”
opinion
Report
ads
Newsletter
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!