-
Los Angeles Fires in California Described as..Apocalyptic
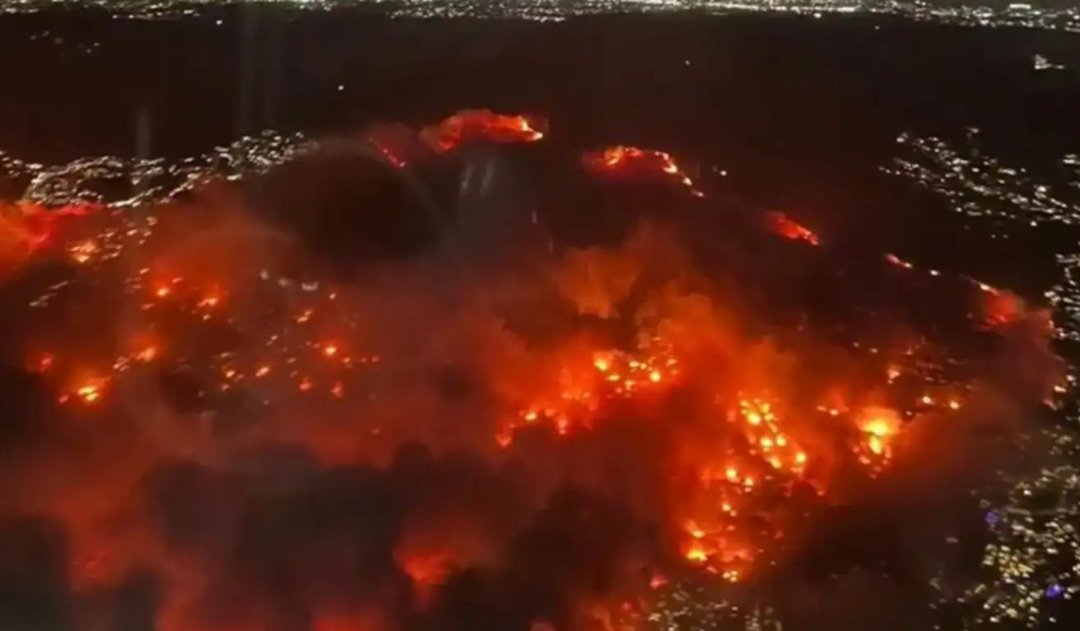

The city of Los Angeles, California, has been battling ongoing wildfires since January 7, resulting in the deaths of 10 people and forcing over 360,000 residents to evacuate their homes under mandatory orders.
Survivors have described the scene as “almost like the end of the world,” with entire neighborhoods reduced to ash, leaving residents in a state of grief and shock. Oren Waters, one of the survivors, told Agence France-Presse, "This is unimaginable. Everything around us is destroyed."
As wildfires continue to spread across California, impacting around 10,000 structures in coastal Los Angeles, the issue of freshwater scarcity has emerged, limiting firefighting efforts. With the state boasting a significant coastline along the Pacific Ocean, many are questioning why the U.S. does not utilize ocean water to combat these fires.
This article addresses that question, according to the science news site Technology Org.
To extinguish a fire, one must reduce at least one of the three elements required for combustion: heat, fuel, or oxygen. When water is used, a significant amount of heat is absorbed to facilitate evaporation, which helps cool and weaken the fire, while also suffocating it by cutting off its oxygen supply.
Although the difference in the impact of freshwater and saltwater isn’t huge on a fundamental level, saltwater is typically not used for various reasons. Components of water tanks and other firefighting equipment are made from metals that can corrode due to salt. Additionally, saltwater damages vegetation, rendering soils unproductive for many years.
In theory, saltwater could be used in coastal cities devoid of vegetation, but the firefighting systems predominantly rely on freshwater, making its use impractical even in those scenarios.
Overall, freshwater is more effective in extinguishing fires due to its chemical properties. The salt content in saltwater interferes with the firefighting process, making it less effective, alongside being corrosive, which can harm firefighting equipment.
Moreover, saltwater is a good conductor of electricity, making its use in electrical fires risky due to increased shock hazards.
For these reasons, freshwater remains the preferred option for firefighting efforts, even though specialized extinguishing agents may be required for certain types of fires. However, if freshwater is not available, using saltwater is always better than doing nothing at all.
Finally, saltwater is harmful to plants due to its high salt content, specifically sodium chloride, which leads to a phenomenon known as soil salinization. Excess salt remains in the soil after firefighting efforts, causing potentially lethal damage to vegetation.
You May Also Like
Popular Posts
Caricature
BENEFIT Sponsors BuildHer...
- April 23, 2025
BENEFIT, the Kingdom’s innovator and leading company in Fintech and electronic financial transactions service, has sponsored the BuildHer CityHack 2025 Hackathon, a two-day event spearheaded by the College of Engineering and Technology at the Royal University for Women (RUW).
Aimed at secondary school students, the event brought together a distinguished group of academic professionals and technology experts to mentor and inspire young participants.
More than 100 high school students from across the Kingdom of Bahrain took part in the hackathon, which featured an intensive programme of training workshops and hands-on sessions. These activities were tailored to enhance participants’ critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving, and team-building capabilities, while also encouraging the development of practical and sustainable solutions to contemporary challenges using modern technological tools.
BENEFIT’s Chief Executive Mr. Abdulwahed AlJanahi, commented: “Our support for this educational hackathon reflects our long-term strategic vision to nurture the talents of emerging national youth and empower the next generation of accomplished female leaders in technology. By fostering creativity and innovation, we aim to contribute meaningfully to Bahrain’s comprehensive development goals and align with the aspirations outlined in the Kingdom’s Vision 2030—an ambition in which BENEFIT plays a central role.”
Professor Riyadh Yousif Hamzah, President of the Royal University for Women, commented: “This initiative reflects our commitment to advancing women in STEM fields. We're cultivating a generation of creative, solution-driven female leaders who will drive national development. Our partnership with BENEFIT exemplifies the powerful synergy between academia and private sector in supporting educational innovation.”
Hanan Abdulla Hasan, Senior Manager, PR & Communication at BENEFIT, said: “We are honoured to collaborate with RUW in supporting this remarkable technology-focused event. It highlights our commitment to social responsibility, and our ongoing efforts to enhance the digital and innovation capabilities of young Bahraini women and foster their ability to harness technological tools in the service of a smarter, more sustainable future.”
For his part, Dr. Humam ElAgha, Acting Dean of the College of Engineering and Technology at the University, said: “BuildHer CityHack 2025 embodies our hands-on approach to education. By tackling real-world problems through creative thinking and sustainable solutions, we're preparing women to thrive in the knowledge economy – a cornerstone of the University's vision.”
opinion
Report
ads
Newsletter
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!