-
Drought blamed for dozens of cow poisoning deaths in northwest Italy
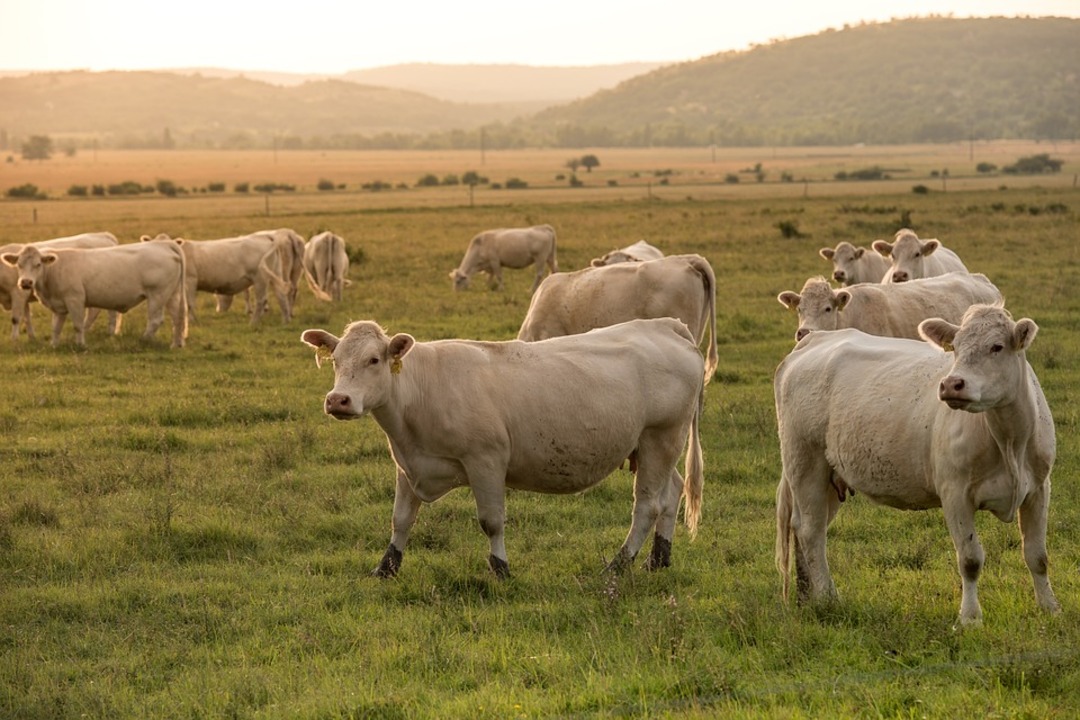

Experts blamed drought for an open-air morgue on an Italian farm earlier this month after around 50 cows were poisoned by young sorghum plants.
The Piedmontese cattle on the farm in Sommariva del Bosco, near Turin in northwest Italy, died suddenly due to acute prussic acid poisoning on August 6, according to the local IZS animal welfare body, according to the al-Arabiya English, the AFP reported,
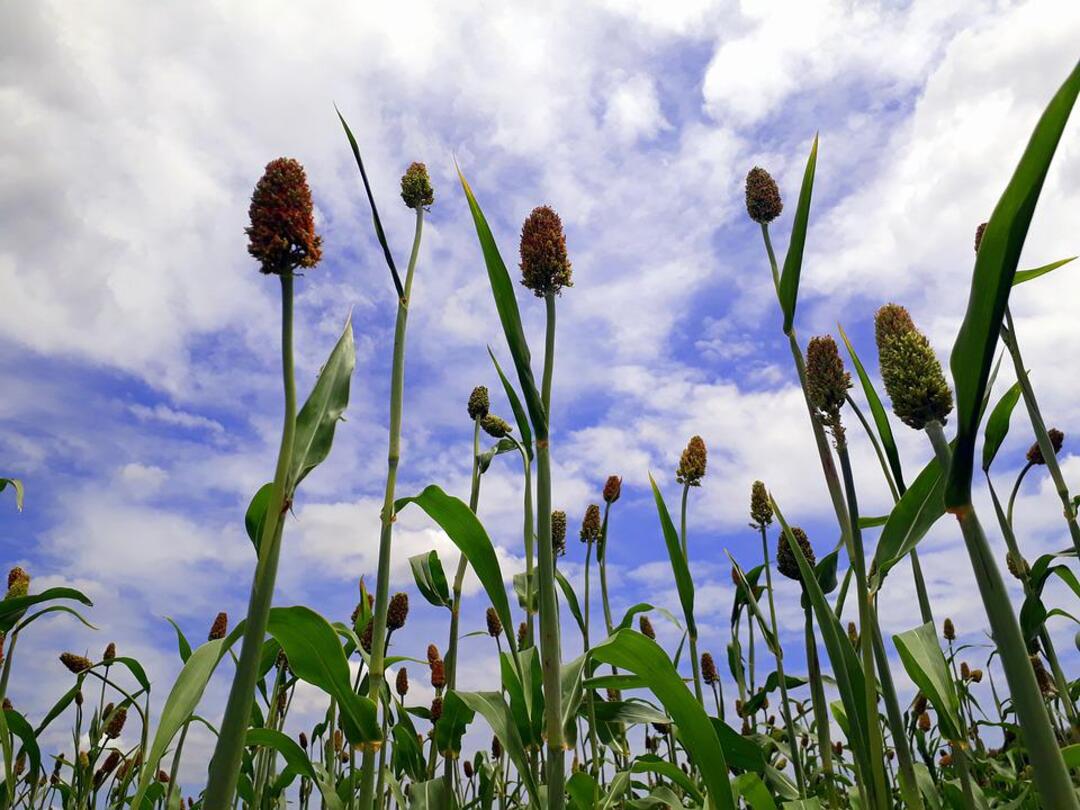
This acid comes from dhurrin, which is naturally present in young sorghum plants, although not in the same high concentrations as those found in samples taken at the site.
“We suspect that the drought caused this very large quantity of dhurrin within the sorghum plants,” said Stefano Giantin, a vet at the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale for northwest Italy, who is on the case.
With normal growing plants, the amount of dhurrin would lower as the plants grew larger. But since the ongoing drought has stunted the growth of sorghum plants, dhurrin has concentrated inside them.

Prussic acid poisoning in cattle is quick and brutal, with symptoms occurring 10-15 minutes after ingestion and death some 15-30 minutes later. It causes respiratory, nervous and muscular disorders.
Dhurrin naturally occurs in sorghum, particularly in young shoots that use it as a defense against herbivores, but when digested, releases prussic acid, also known as hydrogen cyanide.
China takes action to alleviate drought as record heatwave continues
But “normally, it doesn’t cause death,” Giantin told AFP.
In the samples taken from Sommariva del Bosco, the concentration of dhurrin in the shoots was at an unusually high level, which Giantin said appeared to be the result of the drought that has hit Italy and much of Europe this summer.
A dose of more than 700 mg/kg of prussic acid is considered fatal for cattle, but the animals at Sommariva were found to have quantities of more than 900 mg/kg in their blood.
Italian cities of Verona and Pisa limit water usage amid drought
The only way of saving affected cows is to inject them with sodium thiosulfate, to neutralize the hydrogen cyanide.
With this, experts were able to save around 30 cows on August 11, when three more farms in Piedmont were hit by the same phenomenon – although not before 14 died.
Source: alarabiyaenglish
You May Also Like
Popular Posts
Caricature
BENEFIT Sponsors BuildHer...
- April 23, 2025
BENEFIT, the Kingdom’s innovator and leading company in Fintech and electronic financial transactions service, has sponsored the BuildHer CityHack 2025 Hackathon, a two-day event spearheaded by the College of Engineering and Technology at the Royal University for Women (RUW).
Aimed at secondary school students, the event brought together a distinguished group of academic professionals and technology experts to mentor and inspire young participants.
More than 100 high school students from across the Kingdom of Bahrain took part in the hackathon, which featured an intensive programme of training workshops and hands-on sessions. These activities were tailored to enhance participants’ critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving, and team-building capabilities, while also encouraging the development of practical and sustainable solutions to contemporary challenges using modern technological tools.
BENEFIT’s Chief Executive Mr. Abdulwahed AlJanahi, commented: “Our support for this educational hackathon reflects our long-term strategic vision to nurture the talents of emerging national youth and empower the next generation of accomplished female leaders in technology. By fostering creativity and innovation, we aim to contribute meaningfully to Bahrain’s comprehensive development goals and align with the aspirations outlined in the Kingdom’s Vision 2030—an ambition in which BENEFIT plays a central role.”
Professor Riyadh Yousif Hamzah, President of the Royal University for Women, commented: “This initiative reflects our commitment to advancing women in STEM fields. We're cultivating a generation of creative, solution-driven female leaders who will drive national development. Our partnership with BENEFIT exemplifies the powerful synergy between academia and private sector in supporting educational innovation.”
Hanan Abdulla Hasan, Senior Manager, PR & Communication at BENEFIT, said: “We are honoured to collaborate with RUW in supporting this remarkable technology-focused event. It highlights our commitment to social responsibility, and our ongoing efforts to enhance the digital and innovation capabilities of young Bahraini women and foster their ability to harness technological tools in the service of a smarter, more sustainable future.”
For his part, Dr. Humam ElAgha, Acting Dean of the College of Engineering and Technology at the University, said: “BuildHer CityHack 2025 embodies our hands-on approach to education. By tackling real-world problems through creative thinking and sustainable solutions, we're preparing women to thrive in the knowledge economy – a cornerstone of the University's vision.”
opinion
Report
ads
Newsletter
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!