-
Under Bashar al-Assad's Rule: 830 Foreign Military Sites in Syria

This report presents maps illustrating the distribution of foreign military bases in Syria, examining the presence of various foreign powers, including the U.S.-led international coalition, Russia, Turkey, Iran, and Hezbollah.
The report relies on maps prepared by the Syrian "Jusoor for Studies Center," which depict the locations of military sites occupied by various international forces directly intervening in Syria. By the end of the first half of 2022, the total number of these foreign bases and military points reached 830, distributed as follows: U.S.-led coalition: 30 sites; Turkish forces: 125 sites; Russian forces: 105 sites; Iranian forces: 570 sites.
The coalition has established 30 military sites, including bases and outposts, across six governorates: 17 in Hasakah, 9 in Deir ez-Zor, one base in Raqqa, one base in the rural Damascus, one in Homs, and another in Aleppo.
The presence of the international coalition in eastern Syria poses a barrier to the expansion of Russian and Iranian influence. Meanwhile, Israel maintains a distinct presence through ongoing airstrikes against "Iranian targets" in Syria. There are understandings among foreign powers to regulate their relations and "prevent clashes."
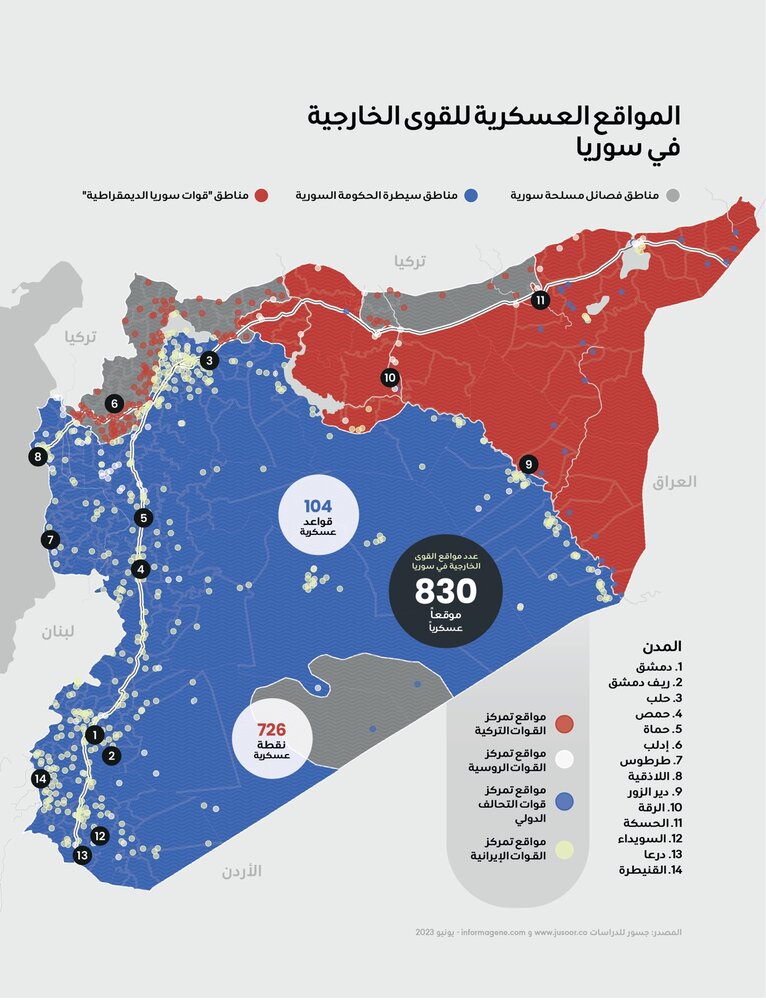
The new study of foreign military sites in Syria reveals an overall increase in the number of bases and military points for all foreign powers, with the exception of Turkey and the U.S., which have largely maintained the number and locations of their posts. There has been a slight increase in Russian presence; however, Iran has experienced the greatest growth in the number of sites and area of deployment during the first half of 2022. This marks the largest foreign military presence in Syria's history, reflecting the extent of external influence compared to the diminishing role of Syrians themselves in altering the course of their country's situation.
Since the outbreak of the war in Syria in 2011, sparked by massive anti-regime demonstrations, multiple countries have intervened to support the Syrian government on one side and opposition factions on the other. Foreign intervention includes political, military, and operational support for parties engaged in the Syrian conflict, in addition to active foreign involvement. Most parties involved in the war have received support, whether military, logistical, or diplomatic, from foreign states and entities.
The "Jusoor for Studies Center" has documented the locations of Iranian forces across various Syrian provinces, amounting to 570 military sites. These bases serve as centers for decision-making regarding military operations in Syria, whether for the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps or other affiliated militias. The data indicates that the numbers and distribution of these forces provide them with a substantial degree of influence and control, often surpassing that of government forces.
In an interview with Russian media last March, President Bashar al-Assad confirmed that "the increase in the number of Russian military bases in Syrian territory may be necessary in the future, as Russia's presence in Syria is tied to the global balance of power." Assad stated, "The view of military bases should not be solely linked to the issue of combating terrorism; the fight against terrorism is currently ongoing but will be temporary. The Russian military presence in any country cannot be based on something temporary; we are talking about international balance... Russia's presence in Syria has significance related to the balance of power in the world."
You May Also Like
Popular Posts
Caricature
Qatar Closes Hamas Office...
- November 11, 2024

Qatar Closes Hamas Offices
opinion
Report
ads
Newsletter
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!






















